Certificates have become a key component in today’s cyberspace, where each component requires a certificate to confirm its identity. From users to servers to applications, every part of the organization requires a certificate to function as intended. While this enhances the organization’s overall security, as the organization grows, it becomes difficult to manage such certificates, which include renewing them, revoking them, and sometimes issuing certificates on a large scale.
While MDM solutions like Intune can make it easier to issue required certificates to machines and technologies like auto-enrollment can provide certificates to users and machines as well, the problem arises when we need to issue those certificates to servers and applications.
PKI serves as the backbone of these certificates. While some certificates are issued by public CAs, the majority of the certificates are issued by private CAs, and managing such private CAs becomes the responsibility of the SOC team (or other security team), which increases the operational complexity of the overall process.
In this blog, let us take a deeper dive into the world of certificate management, some of the best practices, some common challenges, and finally, how Encryption Consulting can help with their expertise, as well as with our own CertSecure Manager solution.
What is a Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM) solution?
As we already established above, every organization needs a proper, valid certificate to function, which is trusted by the whole organization. These certificates would be issued to end-entities such as users, computers, networking equipment, servers, applications, and so on. If the underlying PKI, which is providing trust and visibility of these certificates, is facing an outage, then none of the components of the organization will work. Employees cannot get into buildings without proper smartcards, people cannot use VPNs, machines, servers, and applications will cease functioning, and it will be complete chaos.
Managing these certificates and their underlying infrastructure is crucial for the organization to function normally. These certificates go through phases from issuance to revocation, where each phase of the lifecycle is crucial for the organization to maintain properly. And if a certificate that is about to expire isn’t monitored or renewed in a timely manner, then it may cause unforeseen outages in the server/application using said certificate. Hence, proper monitoring, ownership, and renewal of certificates become important.
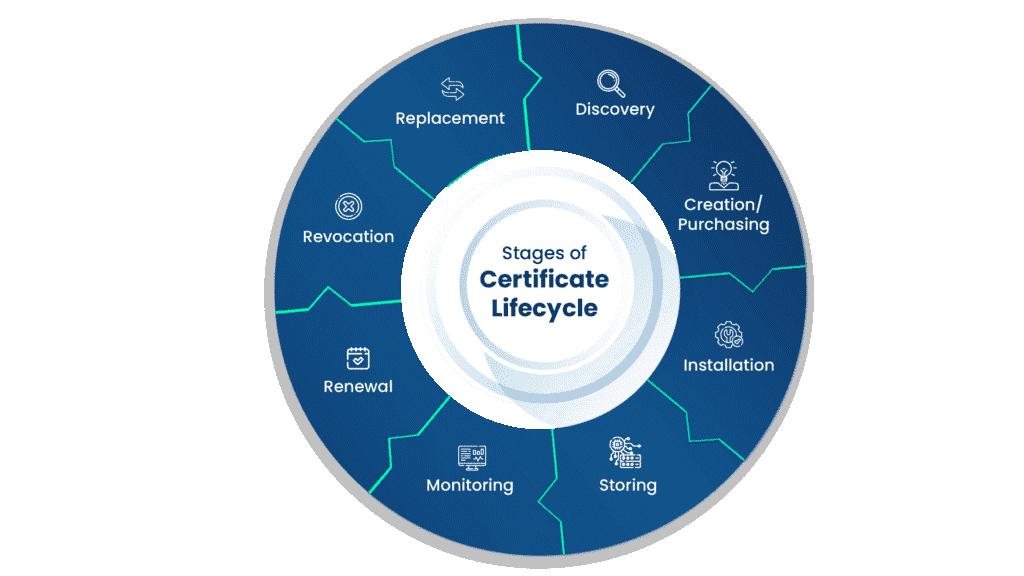
The stages of the certificate lifecycle are as follows:
-
Discovery
The discovery phase of the certificate lifecycle involves searching the network for missing, expired, compromised, or unused certificates that must be revoked, renewed, or replaced. This is an important part of the process, as it finds gaps in the security of certificates and relays these gaps to the monitoring phase, allowing for the sealing of these breaches. Normally, this phase also deals with the inventorying of certificates to help in future Discovery phases, along with any certificate audits that may occur.
-
Creation/Purchasing
This is the phase where the certificate is created. An online user, organization, or device requests a certificate from a Certificate Authority, which contains the public key and other enrollment information needed to enroll the user. The Certificate Authority used to create the certificate can be owned by the organization that desires the certificate or by a third party. If the certificate is obtained from a third party, then it must be purchased from them.
-
Installation
The installation of the certificate is straightforward, but still just as important. The certificate must be installed in a secure, but reachable, location, as users attempting to verify the authenticity of the certificate must have access to it. When the certificate is installed, the CA puts policies in place to ensure the security and proper handling of the certificate.
-
Storage
As previously mentioned, when the certificate is installed, it must be in a secure location to prevent compromise. It should not, however, be so secure that the users who need to read the certificate cannot reach it. The proper policies and regulations to implement for the storage of certificates will be discussed later in this document.
-
Monitoring
Monitoring is one of the most important stages of the certificate lifecycle. This is an almost constant phase where the certificate management systems, whether automatic or manual, watch for breaches, expirations, or compromises of digital certificates. The Monitoring stage uses the inventory created in the Discovery phase to keep track of when certificates should be revoked, renewed, or replaced. The certificate management system then moves those certificates to the next phase, which can be renewal, revocation, or replacement.
-
Renewal
Renewal of a certificate occurs when the expiry date of the certificate is reached. This occurs naturally with certificates, as best practice is not to use a certificate for more than 5 years at the most. Certificates can be set to renew automatically, or a list can be kept of certificate expiration dates, and the administrator of the certificates can renew them at the proper time.
-
Revocation
If a certificate is found to be compromised, stolen, or otherwise negatively affected, then that certificate will be revoked. When a certificate is revoked, it is put on a Certificate Revocation List (CRL). This list ensures that other CAs know that this is no longer a valid certificate.
-
Replacement
The certificate is replaced when users switch from paying for certificates to creating their own Public Key Infrastructures (PKIs) and CAs. This is rarely done, as renewing a certificate from the original provider is much easier than replacing it.
Common Challenges for Organizations Without CLM
With Microsoft AD CS being widely used in the industry with no proper CLM solution built with it, many organizations often face some challenges while operating their private as well as their public PKI, such as Digicert:
-
Manual CLM
Without a proper CLM solution, teams are often responsible for issuing, renewing, and revoking certificates manually, tracking their owners, and renewing them in a timely manner before expiration. This type of process is prone to human error, which can lead to outages and operational inefficiencies.
-
Lack of central visibility/Purchasing
Organizations tend to have multiple CAs, including at least one Microsoft CA acting as a private CA and one public CA, such as Digicert. Managing certificates from different CAs can often be challenging, as it involves tracking expiring certificates, renewing the certificates separately with their own defined process, and tracking the ownership of the certificates.
-
Limited reporting and insights
ADCS alone may not provide the detailed reporting and insights needed for proactive certificate management. A CLM solution enhances visibility into certificate usage and health.
-
Improper Policy Management
With multiple CAs being used to manage and issue certificates, the implementation of organizational policies and ensuring it is adhered to can seem challenging, as each CAs functions differently, and sometimes there are no mechanisms to apply such policies, making the procedures prone to human errors.
Policy Management during Certificate Issuance and Revocation
Every organization has its internal policies that it needs to abide by. These policies often contain restrictions such as:
- What should be the minimum key size of the certificate?
- What information should be contained inside the certificate, such as organization, Organization unit, etc., and should an email ID be present inside the certificate itself to track its owner?
- The approval process for certain types of certificates is essential. Who should approve the type of certificate before issuance is often inscribed in the policies themselves, including how many approvals are needed for certain types of certificates.
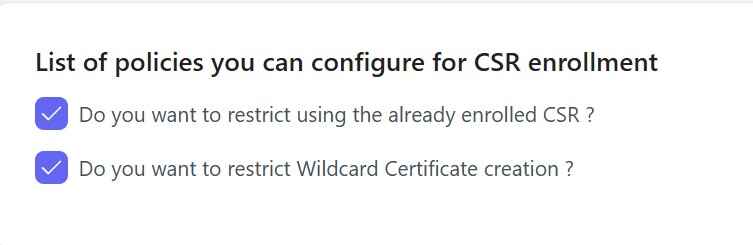
- If wildcard certificates are allowed to be issued.
- If CSR can be reused to issue certificates again
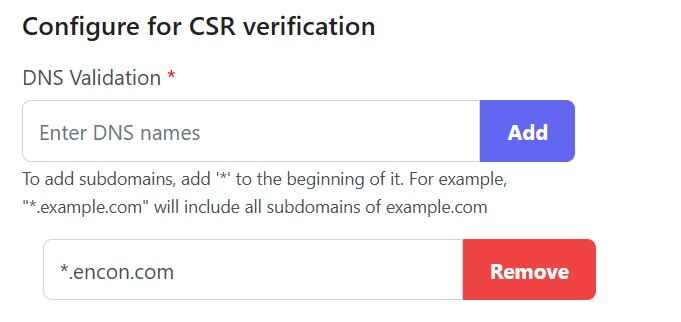
- What domains should be allowed as SAN attributes in the certificate?
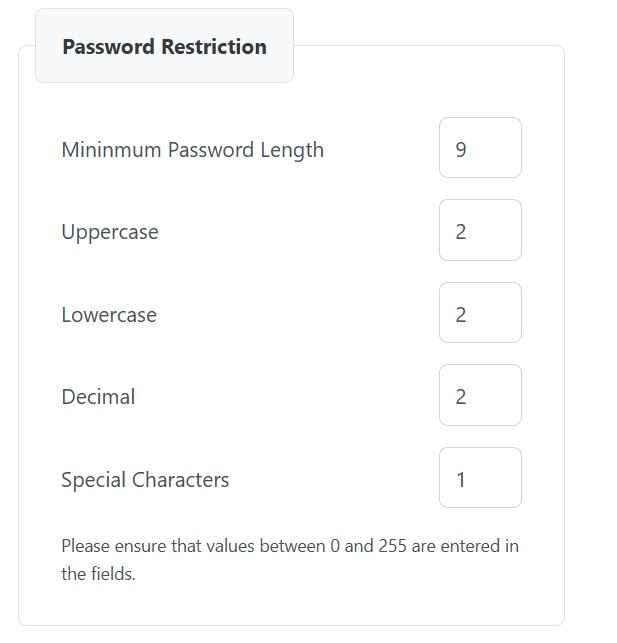
- Password policies in cases of PFX certificate
Governance by these policies can often be challenging for teams not using any CLM solution. We have encountered customers in the past who do not check any of these details or track proper ownership of the certificate. That would significantly increase risks and potential insider attacks within the organization.
CertSecure Manager also includes one-click renewal and revocation procedures, where appropriate owners and admins can renew or revoke a certificate using a single click. After the required permissions certificates are renewed/revoked from the CA, a confirmation message is sent to the owners via email and Teams.
CertSecure Manager: Certificate Lifecycle Management Solution
While interacting with our clients, we learned about many of their issues. While there are many CLM solutions out there, none focus primarily on Microsoft AD CS, which still maintains the operational and monitoring sides of the PKI manually. This motivated us to create our own solution, which would help our customers with the problems they have been encountering with their own CLM solutions.
While constructing our solution, we focused on solving the key challenges first.
1. Automated Lifecycle Management
With CertSecure Manager, clients can integrate renewal agents with their servers, such as Tomcat, Apache, ISS, load balancers such as F5, as well as their own internal applications. This will help the servers and applications rotate certificates automatically without any human intervention, thereby minimizing outages as well as ensuring proper certificates are pushed to the server every time in a timely manner.
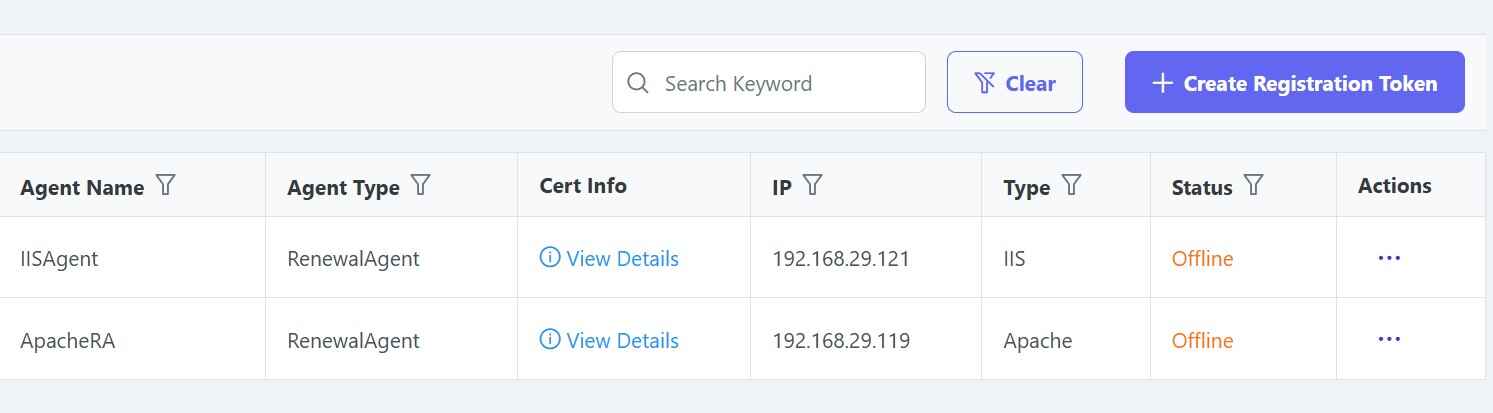
Clients can also integrate their own solutions with ACME or Rest APIs, which will make it easier to get certificates easily for their application.
2. Centralized Visibility and Control
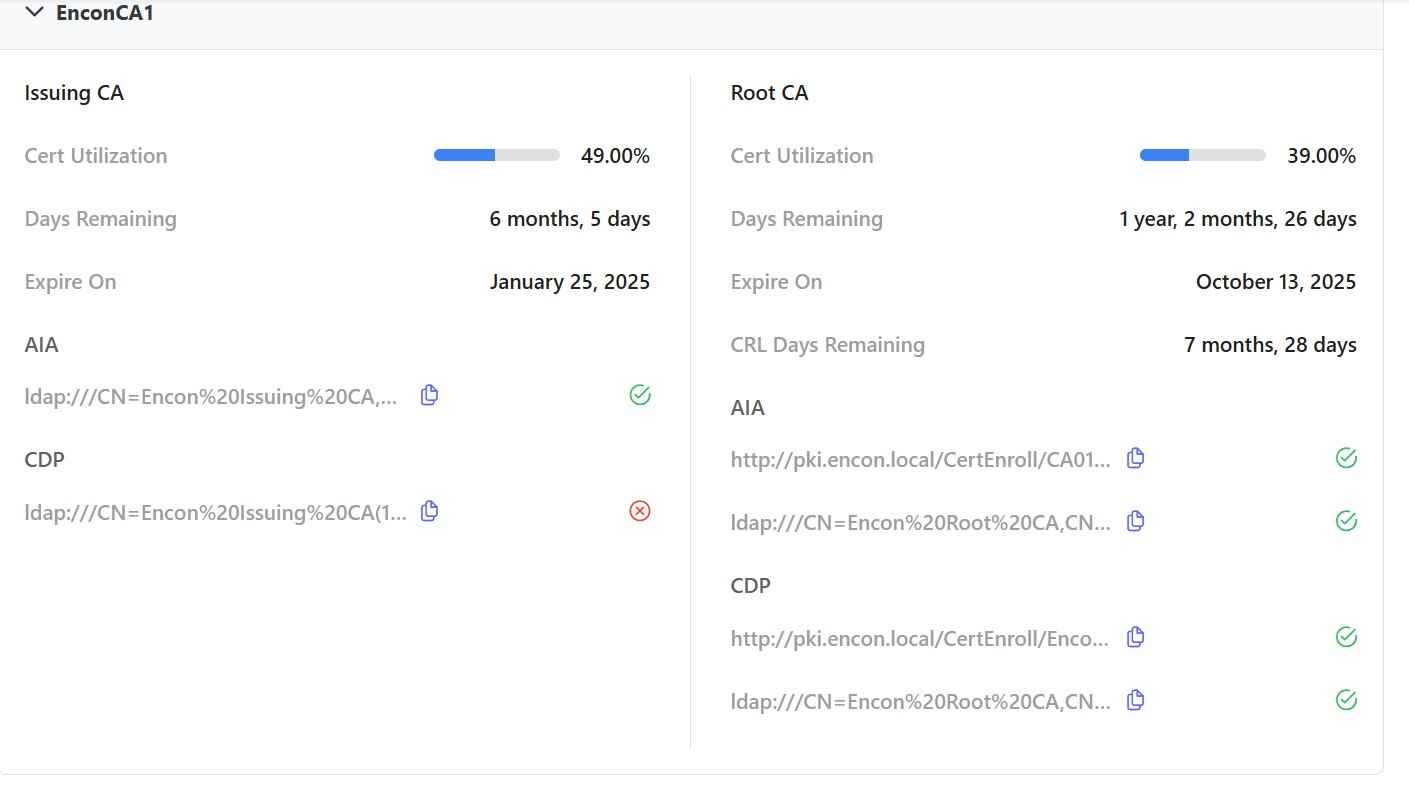
With CertSecure’s HA architecture and connectors, clients can integrate all their CAs with CertSecure with no major network configuration needed. This will ensure that any and all CAs, no matter if they are on cloud or on premises, can be integrated with CertSecure. This will provide a single pane of glass for managing and issuing certificates across multiple private and public CAs.
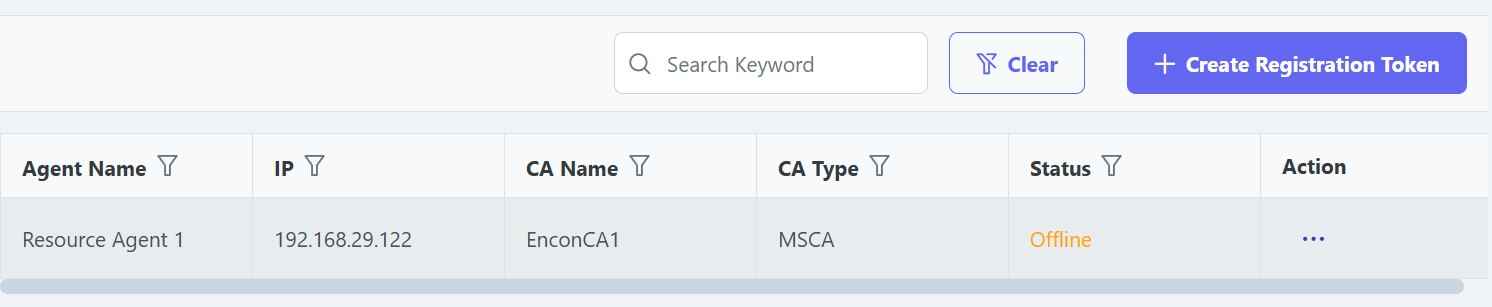
This can also help the operations team monitor their PKI directly from the dashboard. This will help ensure that all CDP/AIA points related to the CA are always active while also providing major updates on CRL and CA certificate renewal.
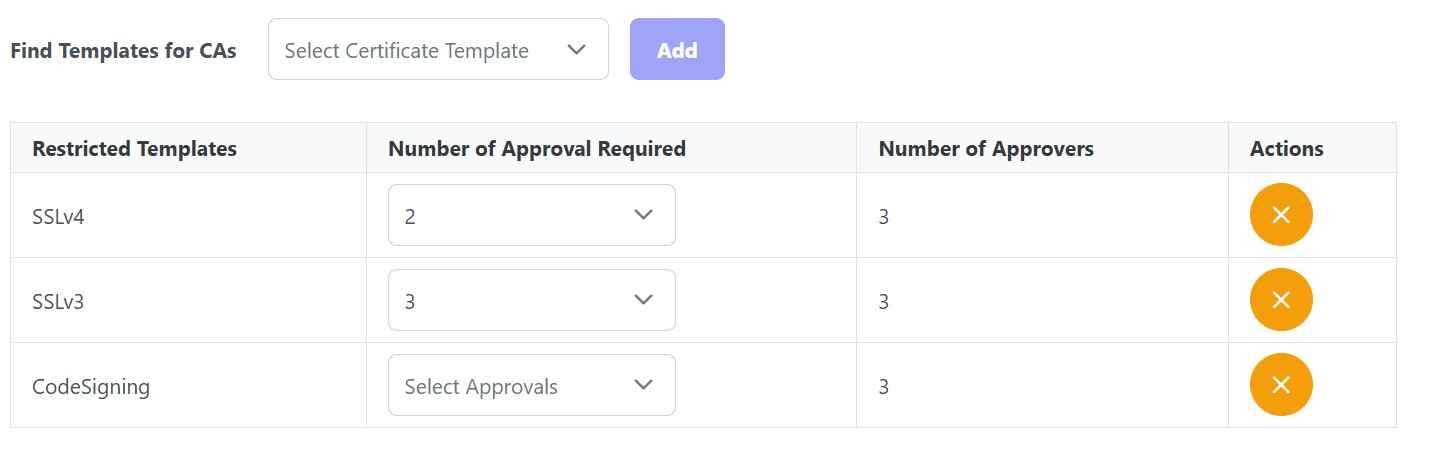
3. Policy Enforcement
CertSecure can help clients set up a policy on a global as well as on a departmental level. This will ensure all users are abiding by the policies defined. These policies help dictate information such as:
a. How many approvals are needed to issue a certificate
b. If CSR can be reused and if users can request wildcard certificates
c. What DNS names are whitelisted, which can be added to the certificates
d. And finally, password policies for the PFX files
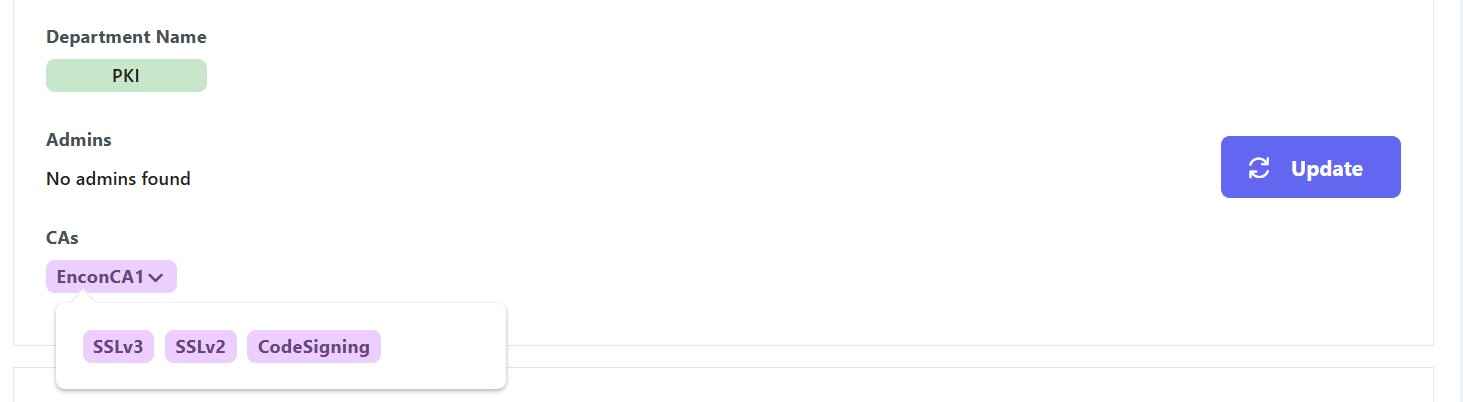
Moreover, we can also define which department gets access to which templates, which creates further restrictions on what templates a user can access. So, for example, the production team will need access to DigiCert, which the development team will not. Similarly, the IT team may need access to web server templates, while they would not need codesigning certificates.
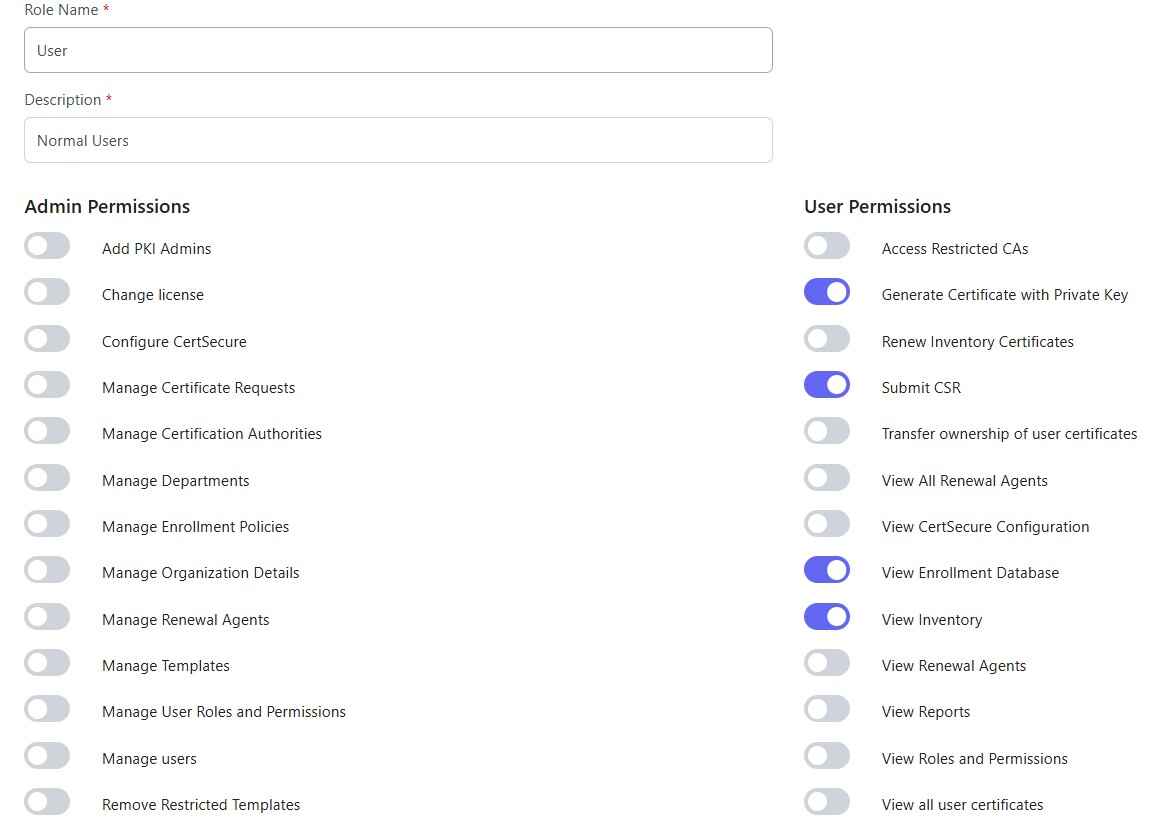
4. Principle of Least Privilege
With policies defined, clients can also define roles that can be assigned to the users. Users can then conduct functions that are only defined by the permissions that are set by the administrator.
5. Comprehensive Monitoring and Alerts
With CertSecure, clients can integrate alerts with Teams, Email, Service Now, with proper escalation protocol to ensure expiring certificates or PKI downtime are brought to attention at the earliest interval. This helps organizations minimize downtime while also having the ease of mind to maintain the security and functionality of the underlying infrastructure, as well as of the certificates it issues.
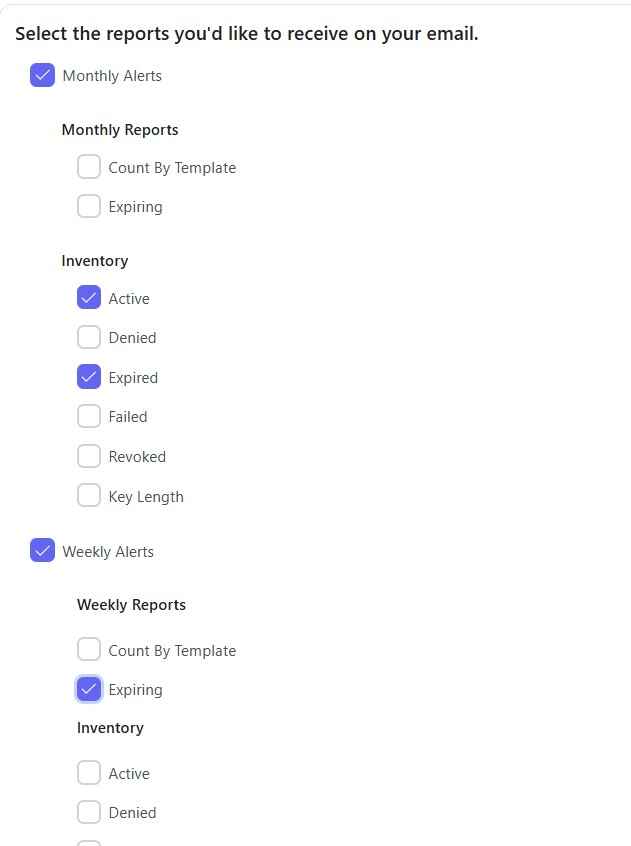
6. Scheduled Reports
With CertSecure, users can schedule reports that will be delivered directly to their emails in a weekly or monthly manner. This will ease the operational side of things as well as provide visibility and a record of operations conducted by the PKI.
7. Easy Onboarding
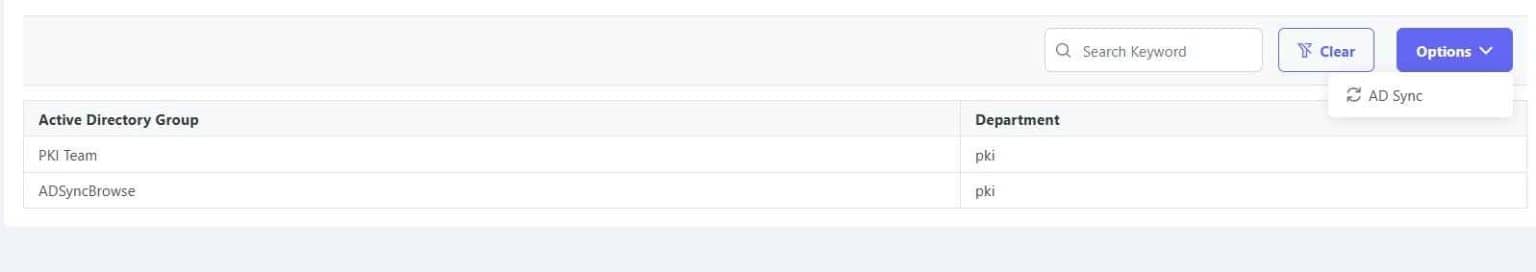
Users can easily be onboarded using AD groups (including Azure AD Groups) into CertSecure, which helps CertSecure monitor and add/remove users as they are added or removed from the group. Deregistering of the user results in transfer of ownership of certificates to department admins, which makes it easier to manage and keep the ownership of certificates, as well as the alerts defined, easier to process.
Conclusion
CertSecure Manager stands out as a comprehensive solution designed to address the complex challenges of CLM. By seamlessly integrating with both private and public Certificate Authorities, CertSecure Manager offers unparalleled centralized visibility and control, empowering organizations to manage their certificates with greater efficiency and security.
Through features like automated lifecycle management, policy enforcement, comprehensive monitoring, and scheduled reporting, CertSecure Manager ensures that your certificate infrastructure is not only robust but also resilient against potential disruptions. Its focus on the principle of least privilege further enhances security, ensuring that users have access only to the resources they need, thereby minimizing the risk of insider threats.
The ease of onboarding, coupled with integrations with Microsoft AD and Azure AD, simplifies user management and streamlines certificate lifecycle processes. With alerts and escalation protocols, CertSecure Manager provides peace of mind, ensuring that critical issues are promptly addressed, minimizing downtime, and maintaining the integrity of your PKI infrastructure.
Encryption Consulting’s commitment to continuous improvement and customer-centric solutions is evident in the development of CertSecure Manager. We remain dedicated to helping organizations achieve higher standards of security, compliance, and operational efficiency. Let CertSecure Manager be your trusted partner in navigating the complexities of certificate management, ensuring that your digital assets remain secure, compliant, and fully operational.
- What is a Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM) solution?
- Common Challenges for Organizations Without CLM
- Policy Management during Certificate Issuance and Revocation
- CertSecure Manager: Certificate Lifecycle Management Solution
- Conclusion




