According to a five-year forecast for IDC Global DataSphere, 2024-2028, it is predicted that the amount of data created, distributed, captured, and consumed will reach 175 ZettaBytes (ZB) by 2025. To understand it better, 1 ZB is equivalent to a trillion Gigabytes (GB). Most of this data is unstructured and needs something that provides it meaning. This is where XML files come into play.
eXtensible Markup Language or XML, is a markup language that establishes rules and organizes any data. It also tells how to store and transport the data over the Internet. XML uses markup symbols or tags, which modern browsers and data processing applications use to process that information.
XML Signing
XML files are used in large numbers, making them an integral part of our web-based applications and technology. But should you trust any XML file? How can you develop confidence in the authenticity of that XML file? You need a digital proof or signature to authenticate and verify its source.
XML signing helps you attach your digital credentials, which will help the receiver fully trust the file’s content. Now, to ease up this process, Encryption Consulting provides you with PKCS#11 Wrapper, which is a software library that provides a Java interface to interact with PKCS#11-compliant devices such as Hardware Security Modules (HSMs), smart cards, or any key vaults.
Along with PKCS#11 Wrapper, we will use the XMLSec tool, a command line tool for signing, verifying, encrypting, and decrypting XML documents.
Configuration of PKCS#11 Wrapper on Ubuntu
Prerequisites
Before we look into the process of XML Signing using XMLSec Tool and our PKCS11 Wrapper in Linux (Ubuntu) machine, ensure the following are ready:
- Ubuntu Version: Ubuntu version 22.04 or later (tested environment is Ubuntu 24.02)
- Dependencies: Install liblog4cxx12 and curl.
To install the dependencies, run the following commands
- sudo apt-get install curl
- sudo apt-get install liblog4cxx12
Installing EC’s PKCS#11 Wrapper
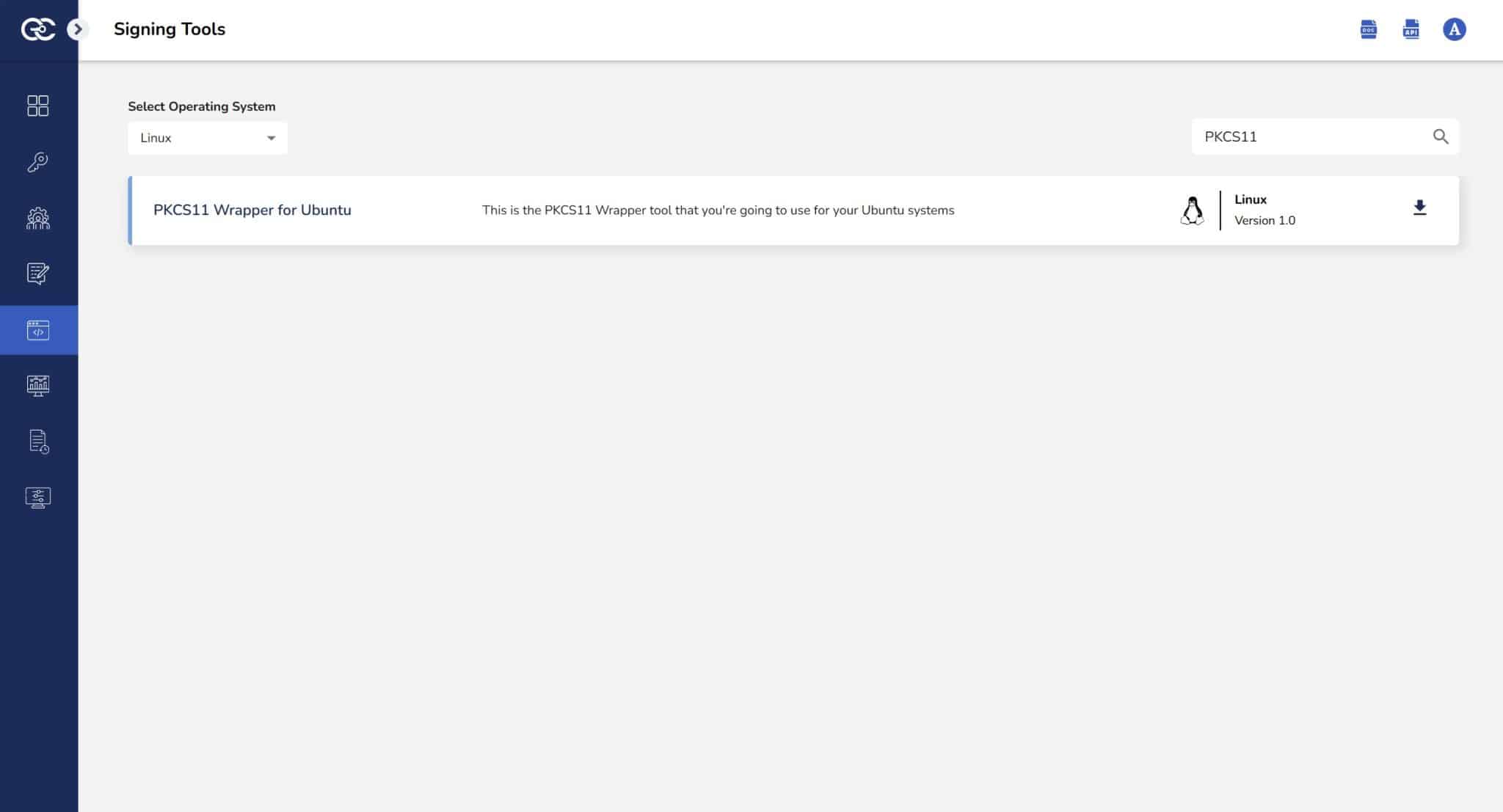
Step 1: Go to EC CodeSign Secure’s v3.01’s Signing Tools section and download the PKCS#11 Wrapper for Ubuntu.
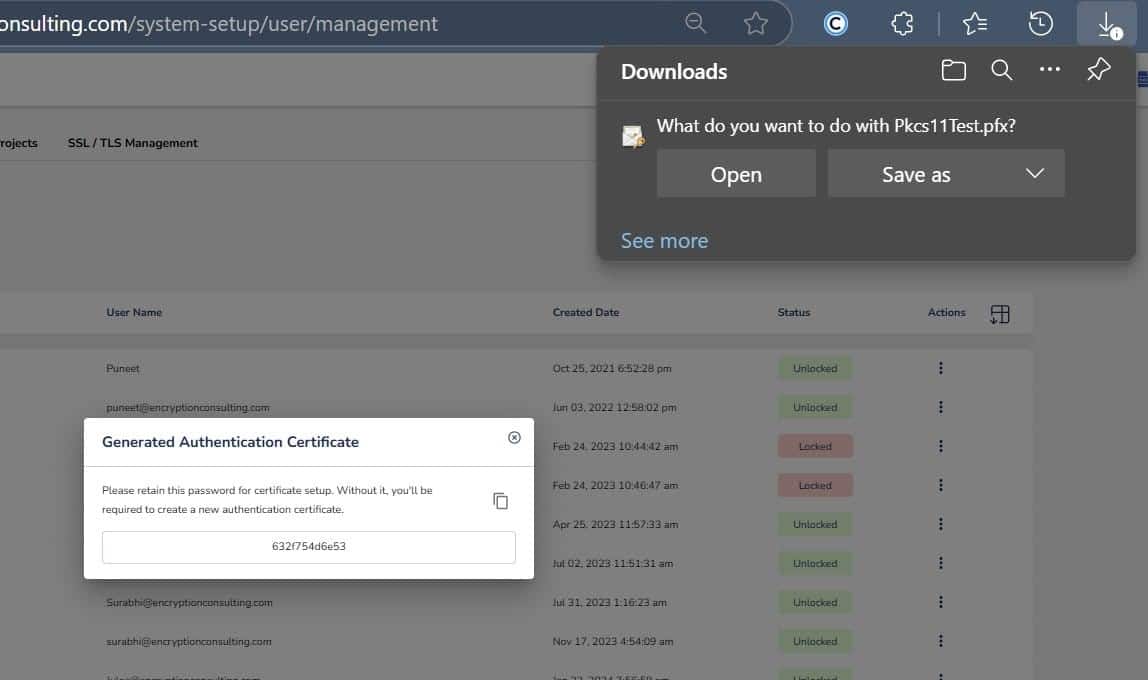
Step 2: After that, generate a P12 Authentication certificate from the System Setup > User > Generate Authentication Certificate dropdown.
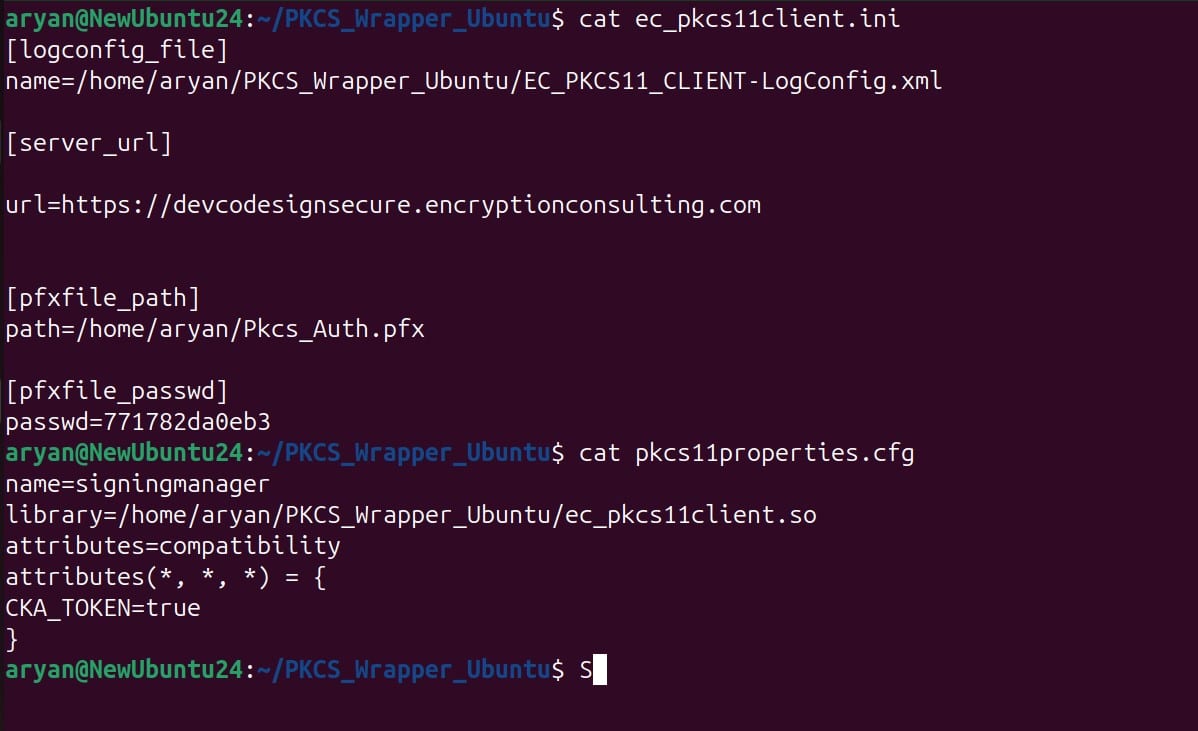
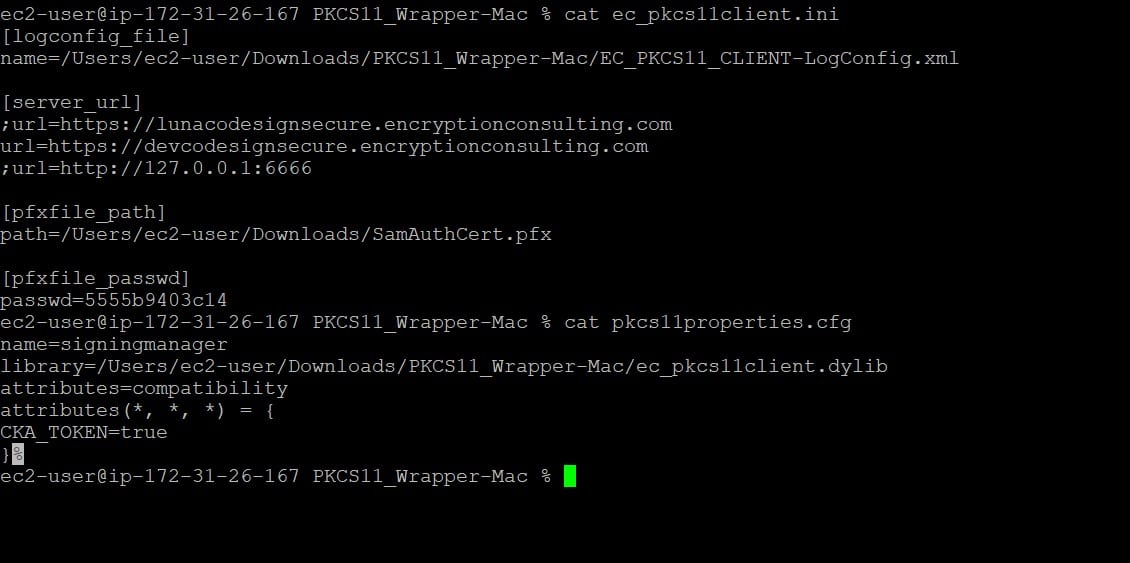
Step 3: Go to your Ubuntu client system and edit the configuration files (ec_PKCS#11client.ini and PKCS#11properties.cfg) downloaded in the PKCS#11 Wrapper.
Installing XMLSec Tool
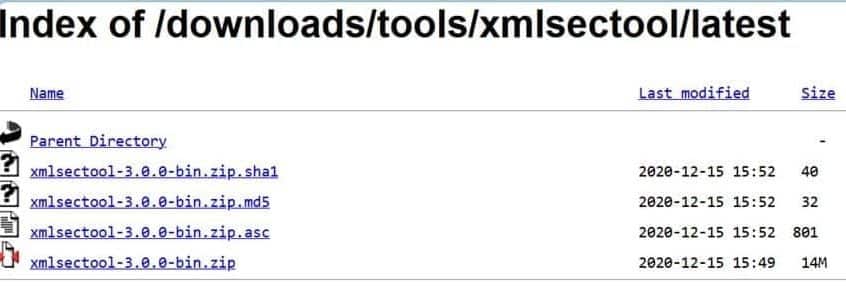
Step 1: Install the latest version of XMLSec Tool (xmlsectool-3.0.0-bin.zip) using this link.
Step 2: You can extract the zip file into a directory of your choice.
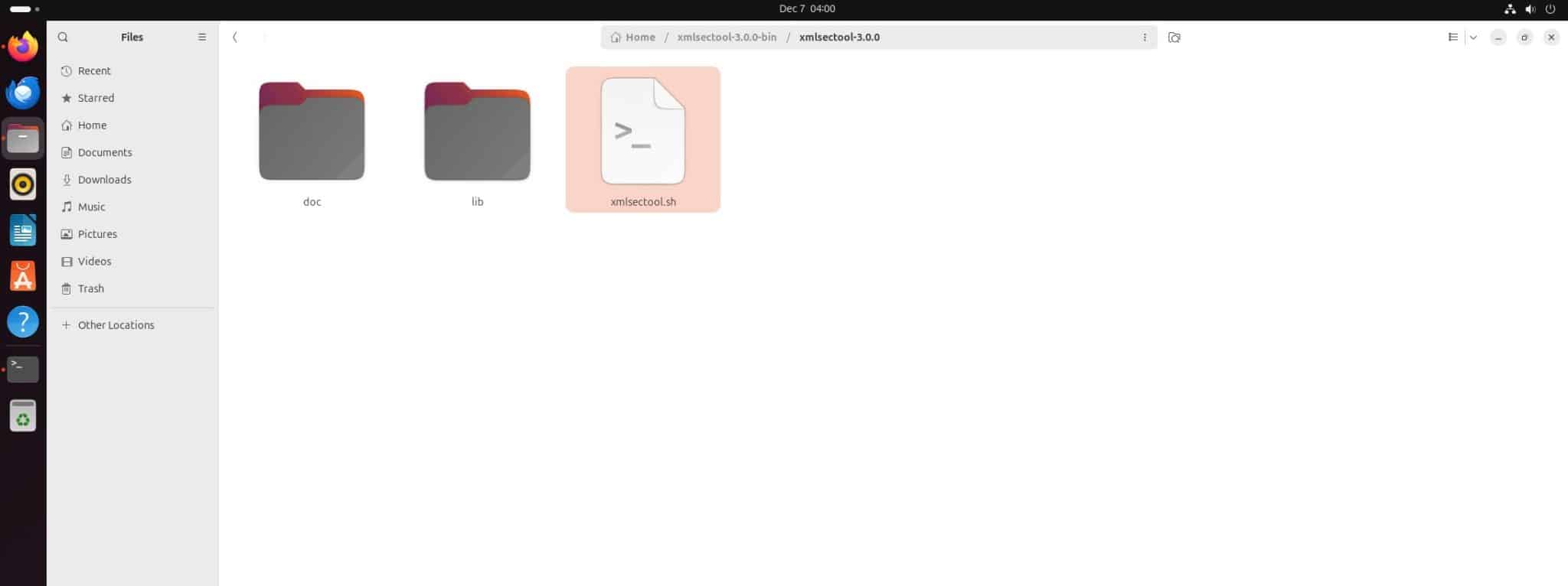
Download and install Java on your Ubuntu machine.
Step 1: Download Amazon Corretto 17 Java (You can check other supported Java versions with XMLSec Tool here.)
wget -O – https://apt.corretto.aws/corretto.key | sudo gpg –dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/corretto-keyring.gpg && \ echo “deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/corretto-keyring.gpg] https://apt.corretto.aws stable main” | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/corretto.list
Step 2: Install Java Package
sudo apt-get update; sudo apt-get install -y java-17-amazon-corretto-jdk
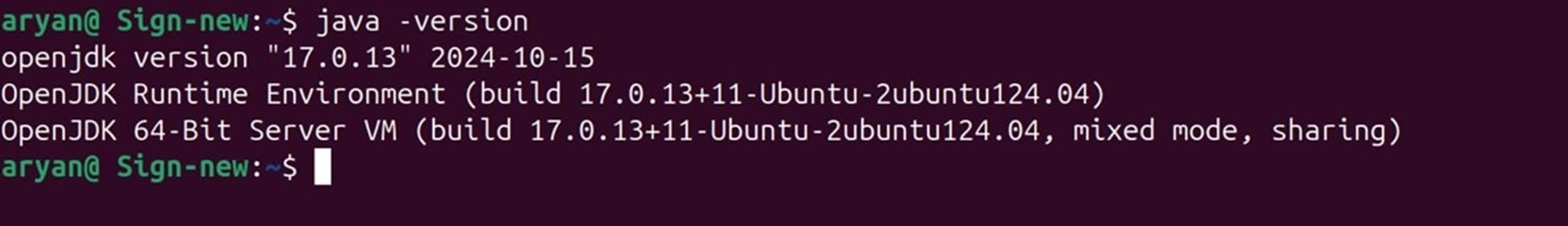
Step 3: Check whether Java has been installed properly or not
java -version
Add Java to Environment Variable
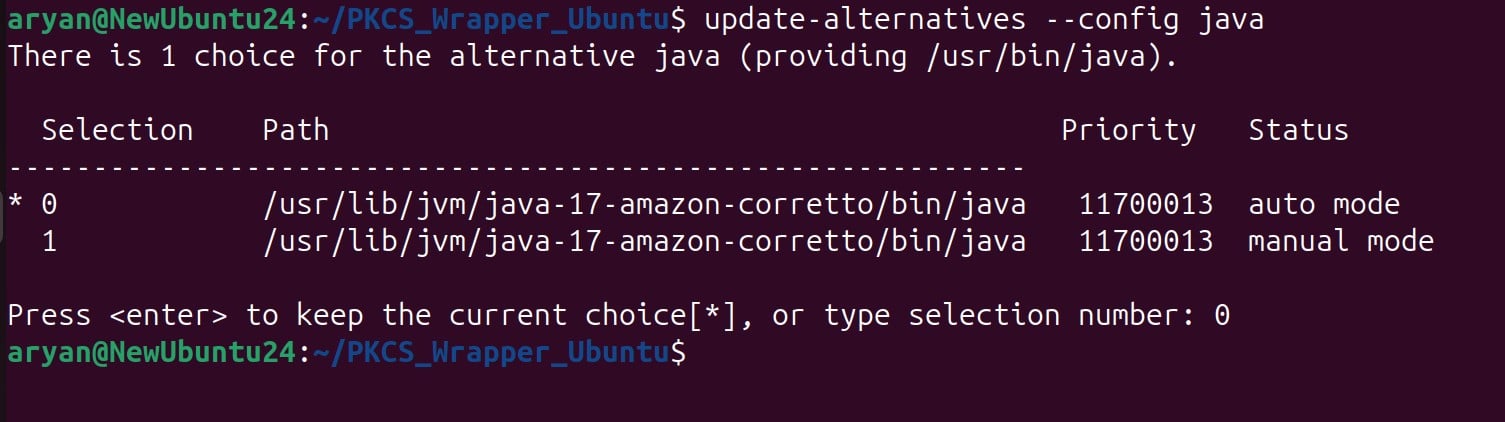
Step 1: Set Amazon Corretto 17 Java as the active version
update-alternatives –config java
Step 2: Add “JAVA_HOME” variable in the ~/.bashrc file
echo “export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-amazon-corretto” >> ~/.bashrc

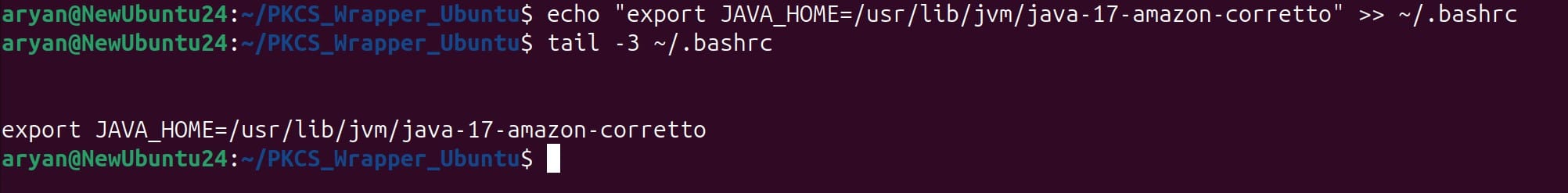
Step 3: Check the ~/.bashrc file
tail -3 ~/.bashrc
Step 4: Reload the Environment variables
source ~/.bashrc
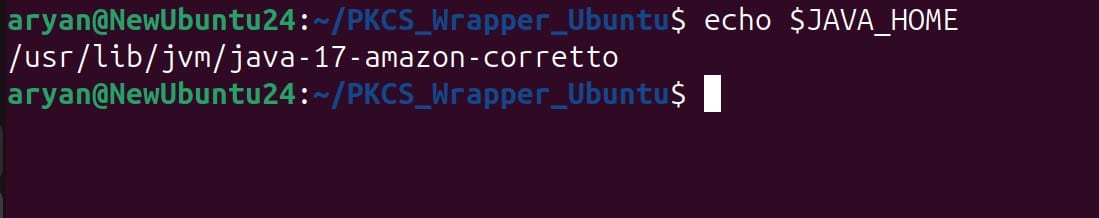
Step 5: Check JAVA_HOME variable value
echo $JAVA_HOME
Signing
Step 1: Change the working directory of the terminal to that folder which contains your “ec_pkcs11client.ini” file.
Step 2: Run the signing command from this directory.
<Path of xmlsectool.sh file> –sign –pkcs11Config <Path of pkcs11properties.cfg> –keyAlias <Key alias of the signing certificate> –keyPassword NONE –inFile <Path of XML file> –outFile <Path of the signed XML file>
A sample command is provided below:
../xmlsectool-3.0.0-bin/xmlsectool-3.0.0/xmlsectool.sh –sign –pkcs11Config pkcs11properties.cfg –keyAlias DemoCertificate –keyPassword NONE –inFile ../xmlSample.xml –outFile ../out-xmlSample.xml
Verification
Run the verification command
<Path of xmlsectool.sh file> –verifySignature –pkcs11Config <Path of pkcs11properties.cfg> –keyAlias <Key alias of the signing certificate> –keyPassword NONE –inFile <Path of the signed XML file>
A sample command is provided below:
../xmlsectool-3.0.0-bin/xmlsectool-3.0.0/xmlsectool.sh –verifySignature –pkcs11Config pkcs11properties.cfg –keyAlias gpg2 –keyPassword NONE –inFile ../out-sample.xml
Configuration of PKCS#11 Wrapper on MacOS
Prerequisites
Before we look into the process of XML Signing using XMLSec Tool and our PKCS#11 Wrapper in MacOS machine, ensure the following are ready:
- MacOS Version: MacOS version 13 (Ventura) or later (tested environment is MacOS 15.1 Sequoia)
- Dependencies: Install liblog4cxx and curl.
To install the dependencies, run the following commands
- brew install log4cxx
- brew install curl
Installing EC’s PKCS#11 Wrapper
Step 1: Go to EC CodeSign Secure’s v3.01’s Signing Tools section and download the PKCS#11 Wrapper for Mac.
Step 2: After that, generate a P12 Authentication certificate from the System Setup > User > Generate Authentication Certificate dropdown.
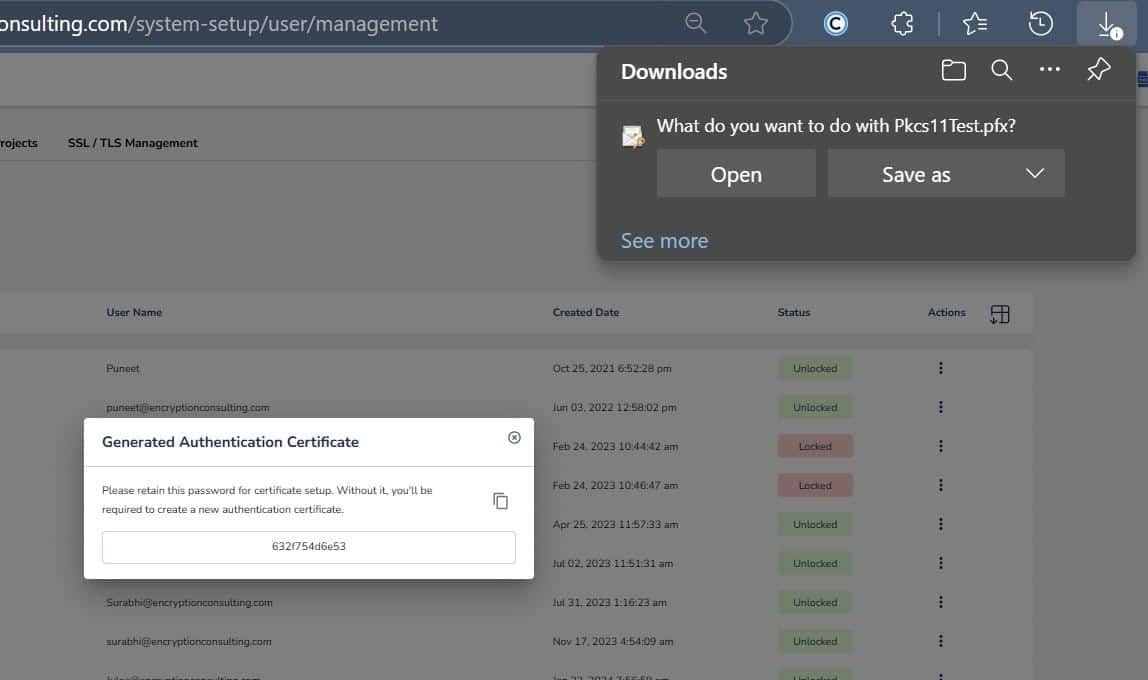
Step 3: Go to your MacOS client system and edit the configuration files (ec_PKCS#11client.ini and PKCS#11properties.cfg) downloaded in the PKCS#11 Wrapper.
Installing XMLSec Tool
Step 1: Download the latest version of XMLSec Tool (xmlsectool-3.0.0-bin.zip) using this link.
You will need this shell file to perform the XML signing
Download and install Java in your MacOS machine.
Step 1: Download Amazon Corretto 17 Java ( You can check other supported Java versions with XMLSec Tool here ).
You can use this link to download the .pkg file for MacOS environment
Step 2: Install Java Package
Begin the installation using the downloaded file.
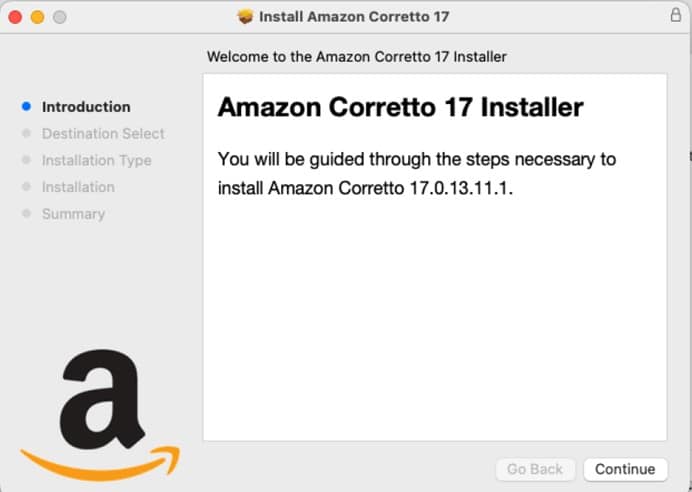
Step 3: Check whether Java has been installed properly or not
java -version
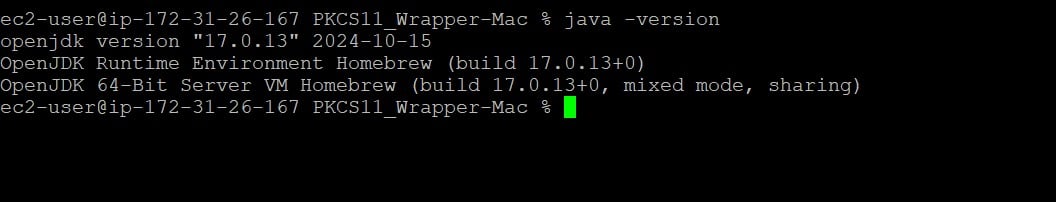
Add Java to Environment Variable
Step 1: Get complete installation path of Amazon Corretto 17 Java
/usr/libexec/java_home –verbose
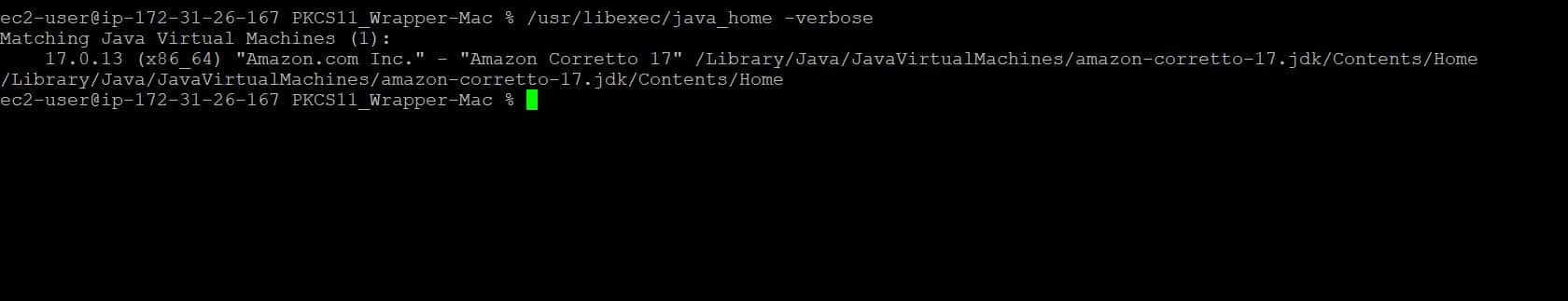
Step 2: Add “JAVA_HOME” variable in the ~/.zshrc file
echo ‘export JAVA_HOME=”/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/amazon-corretto-17.jdk/Contents/Home”‘ >> ~/.zshrc
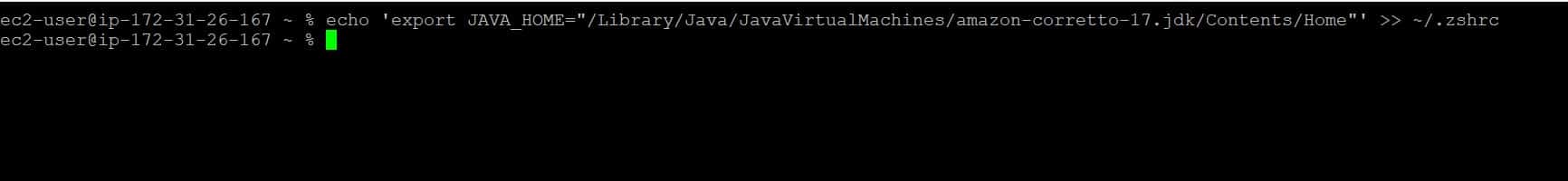
Step 3: Reload the Environment variables
source ~/.zshrc
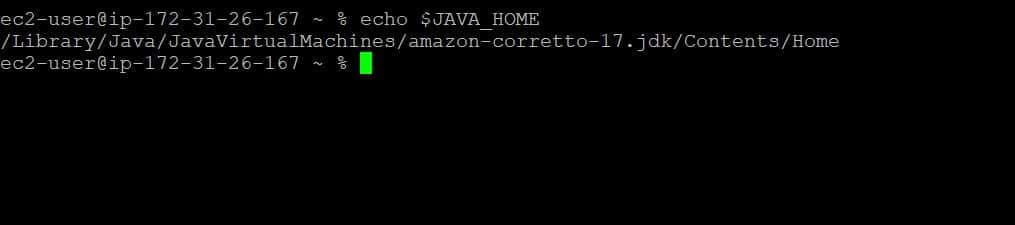
Step 4: Check JAVA_HOME variable value
echo $JAVA_HOME
Signing
Step 1: Change the working directory of the terminal to that folder which contains your “ec_pkcs11client.ini” file.
Step 2: Run the signing command from this directory.
<Path of xmlsectool.sh file> –sign –pkcs11Config <Path of pkcs11properties.cfg> –keyAlias <Key alias of the signing certificate> –keyPassword NONE –inFile <Path of XML file> –outFile <Path of the signed XML file>
A sample command is provided below:
../xmlsectool-3.0.0/xmlsectool.sh –sign –pkcs11Config pkcs11properties.cfg –keyAlias DemoCertificate –keyPassword NONE –inFile ../xmlSample.xml –outFile ../SignedSample.xml
Verification
Run the verification command
<Path of xmlsectool.sh file> –verifySignature –pkcs11Config <Path of pkcs11properties.cfg> –keyAlias <Key alias of the signing certificate> –keyPassword NONE –inFile <Path of the signed XML file>
A sample command is provided below:
../xmlsectool-3.0.0/xmlsectool.sh –verifySignature –pkcs11Config pkcs11properties.cfg –keyAlias gpg2 –keyPassword NONE –inFile ../Signedsample.xml
Conclusion
With unstructured data on the rise, XML document signing is the need of the hour. The seamless integration of our PKCS#11 Wrapper and XMLSec tool offers a flexible and efficient solution for XML document signing.
Using Encryption Consulting’s CodeSign Secure solution, you can build and increase your customer trust. It provides features like client-side hashing, role-based access, and application management to secure your data. It allows you to integrate various DevOps CI/CD pipelines for hands-free, automated code signing.




