Data breaches are security incidents in which unauthorized individuals gain access to and potentially steal or expose sensitive information. They are the most prevalent, highly damaging cyber events, but their costs remain challenging to ascertain due to various factors. These breaches expose physically and electronically sensitive data involving Personally Identifiable Information (PII), medical records, and financial records.
Organizations victimized by data breaches face difficulties and financial burdens in attempting to get back on their feet. Reputationally, the damage can be impossible to overcome as customers stop trusting the services and new customer acquisitions are restricted.
Financially, companies are responsible for many costs – lost sales due to business interruption, fees to notify impacted customers, potential lawsuits and attorney fees, and regulatory fines. The expenses of examining the incident on their behalf, such as forensics and remediation activities, can also be substantial. These factors make data breaches a major concern for organizations of all sizes.
Findings
The recent high-profile cyber-attacks have highlighted the challenges companies face in minimizing the financial and operational impact of these incidents. Every year, the price of a data breach rises as hackers find new ways to attack, new vulnerabilities emerge, and new dangers become apparent.
- According to the 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM, the average cost of a data breach was $4.45 million, a 2.3% increase from the previous year.
- In a survey conducted by Forrester on Security and Risk Management, close to eight of ten or 78 percent of respondents believed their organization’s sensitive data was breached or suffered compromise at least once during the last 12 months.
- Further, 48% of Forrester’s survey respondents have suffered from a breach or other cyber incident that cost more than $1 million. The bulk 27% of these breaches cost anywhere from $2 million to roughly $5 million, while a further 3% had cost over $10 million.
What was the impact of breaches on the industries?
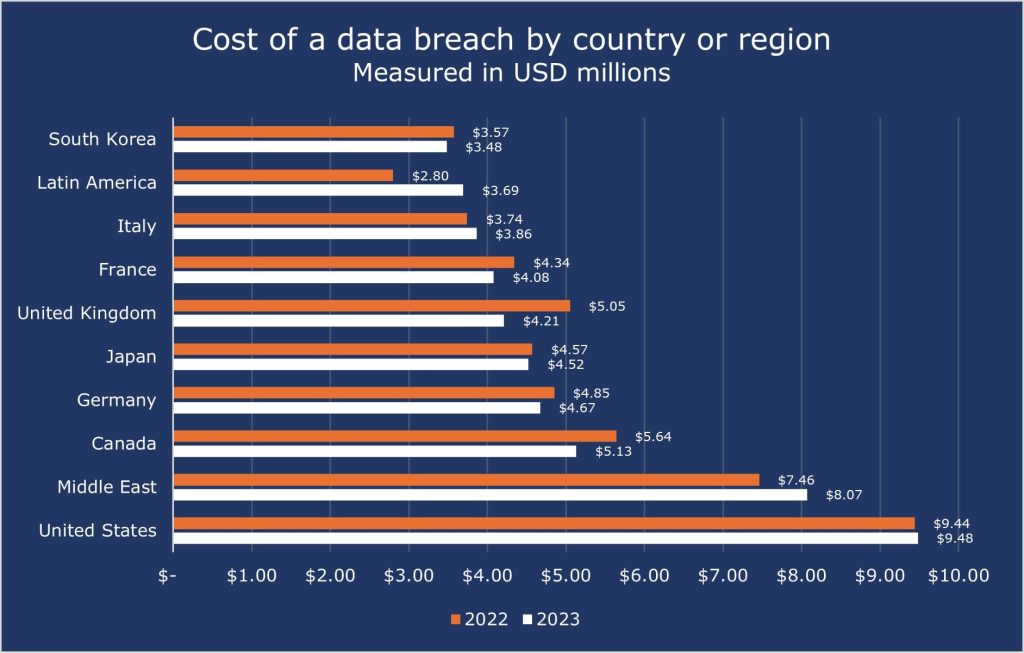
The United States had the highest data breach cost in the world, according to IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023. The USA continues to be among the highest in the world countries, most likely because of the wealth and rigid high level of companies, economy, and amount of data they handle.
One thing to notice for us is the Middle East, which in 2022 had an average of 7.46 million in data breach costs, but in 2023, that becomes 8.07 million, nearly a +8% increase.
The top 5 countries/regions with the costliest data breach price were:
- USA – $9.48 million
- Middle East – $8.07 million
- Canada – $5.13 million
- Germany – $4.67million
- Japan – $4.52 million
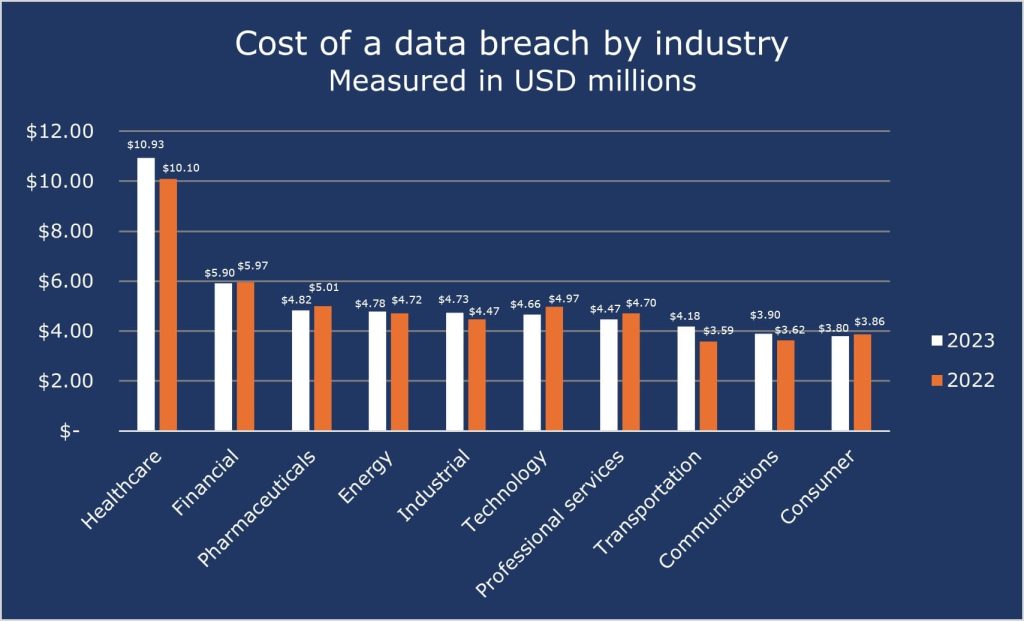
The cost of data breaches in 2023 was highest in the healthcare industry, averaging USD 10.93 million, while the second costliest business – Financials averaged USD 5.9 million. The top five industries with the highest average costs were:
- Healthcare – $10.93 million
- Financials – $5.9 million
- Pharmaceuticals – $4.82 million
- Energy – $4.78 million
- Industrial – $4.73 million
The high cost of data breaches in the healthcare sector can be attributed to several factors.
- Personal Data: The Healthcare industry has the most accurate and detailed information about its customers and employees, making this data and industry a valuable target. Personal information may include medical records, financial records, and location, which are extremely important on the black market.
- Regulations and Fines: The healthcare industry must follow strict rules and laws, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), regarding data privacy and security. HIPAA requires the organization to protect and secure electronic medical data. Any failure to comply with these regulations leads to heavy fines.
Hence, healthcare organizations must use updated IT systems that are less vulnerable to cyber thefts. They should also spend more resources on cybersecurity and train individuals to respond quickly to data breaches.
What Costs Are Involved in a Data Breach?
Moreover, the price of a data breach might become higher than merely paying to recover the lost data. For example, both the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and the CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) impose enormous fines on businesses that allow their consumers’ data to be compromised. Fines are quite substantial, especially for big businesses, and can highly increase the price of the overall data breach.
In case of mismanagement of consumer information, GDPR and CCPA require companies to notify all individuals whose data has been accessed in a specific period. Such a process is quite expensive and includes the fees for lawyers, and overall money spent on sending notifications to potentially millions of customers. All the fines and expenses required to be spent on complying with regulations increase the price of data breaches even more.
According to the study Economic Costs and Impacts of Business Data Breaches, published in Issues in Information Systems, the price of a data breach is made up of direct, indirect, and concealed expenditures and impact factors, which can be divided into business and consumer expenses, such as:
-
Business Costs
These costs are mostly related to financial and operations aspects of the organization and can be divided into two categories:
-
Direct Costs
Expenses under this include sales and functional disturbance costs, financial theft, legal expenses, investigative expenses, regulatory fines, extortion money, PR expenses, monitoring and credit restoration costs, and settlements. Example: British Airways was fined £183.39 million (around USD 232 million) for a data breach in 2020 by GDPR and CCPA regulators.
-
Indirect Costs
These costs include reduced productivity and returns, loss of current and potential customers and market shares, slowed business growth, system downtime, loss of consumers and workers, and loss of competitiveness and confidence, insurance, and reputation. Example: The 2015 Experian data breach compromised thousands of customers’ personal information, resulting in a loss of trust and a damaged reputation for the company.
-
Direct Costs
-
Consumer Costs
These costs are related to the individual user and market aspects of the organization, which also include two categories:
-
Direct Costs
These incorporate financial theft, legal fees, individual extortion payments to thieves, stock price drops, and the additional cost of credit tracking and monitoring decided by the firm. Example: In the 2017 Equifax breach, millions of Social Security numbers were exposed, putting millions of consumers at risk of financial losses. Consumers also faced fraudulent charges or identity thefts as well due to this data breach.
-
Indirect Costs
Indirect costs for consumers will include the loss of time, credit loss, loss of wages, loss of convenience, price increases, joblessness, and emotional pain. Example: Consumers may need to spend time dealing with the aftermath of a breach, such as cancelling credit cards, reporting fraud, and disputing charges. In severe cases, identity theft can lead to job loss, which can be stressful and cause emotional distress.
-
Direct Costs
With so many direct and indirect factors that impact businesses and consumers once a data breach occurs, it’s easy to see why these breaches cost so much. For several companies, the cost of one data breach can be devastating, maybe even resulting in the company closing its doors permanently.
Supply Chain Attacks and Code Signing
Attackers are using sophisticated techniques and exploiting vulnerabilities within supply chains unprecedentedly. A supply chain attack is a type of cyber-attack that targets organizations by focusing on weaker links in a company’s network of all the resources, activities, and technology involved in the development and deployment of a product.
By compromising the supplier’s systems, attackers can inject malicious code into the software, infecting all the customers when they install updates or new software. This can have a devastating impact, as a single compromised supplier can unknowingly put countless organizations at risk.
This highlights the pressing need to strengthen security protocols throughout the software supply chain. The primary motive for cybercriminals is to gain access to sensitive and confidential information that they may misuse to force organizations for financial gain or leak it on the dark web.
Supply chain attacks have become a leading attack vector. They compromise the source code of vendors and suppliers for a greater network of computer systems. In the past, the prime entryway was through stolen credentials or software vulnerabilities, but in recent times, Code signing has acquired a role as a powerful method to prevent any such attacks and breaches.
Code signing is a vital security measure in the fight against supply chain attacks. It is comparable to a digital stamp of acceptance. The code undergoes a cryptographic signing process using a private key held by a trusted entity, such as the software developer or a certificate authority.
A unique digital signature is mathematically linked to the code, which implies the integrity of the source. When a system gets a signed code, it examines the signature utilizing the public key from its signing process. If the signature is valid, the system trusts the signed code.
Code Signing restricts unauthorized or corrupted code from running in a system, making it difficult for attackers to access a network via a supply chain. A valid signature ensures the code originates from a legitimate source, hindering attackers from injecting malicious code disguised as legitimate software updates or applications.
Any modifications to the code after the signing process will invalidate the signature, alerting the system to potential tampering attempts. This enables early detection of compromised code before it can be executed.
CodeSign Secure
Given exploding breach costs and the constant threat of unauthorized code, organizations need powerful solutions to protect their systems. Encryption Consulting LLC’s CodeSign Secure is a strong proactive defence, helping companies minimize the breach risk, diminishing the financial burden.
CodeSign Secure delivers a secure and flexible solution that seamlessly integrates code-signing into on-premises or cloud environments. It integrates with various HSMs to ensure cryptographic keys are always stored in tamper-resistant hardware devices, adding an extra layer of protection against key-related security risks. CodeSign Secure addresses modern software development and distribution needs by ensuring code signing across different operating systems – Windows, Linux, and Macintosh.
CodeSign Secure features multi-layered protection, which incorporates robust code scanning to find vulnerabilities and identify potential malware concealed within the code. Some of its features are:
- Multi-Factor Authentication: The code-signing process is limited to authorized personnel only and requires MFA for an extra layer of security.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): It can register users through the Corporate Active Directory and enables centralized credential and permission management. Additionally, it allows for customizable workflows to grant granular control over code-signing processes, thereby preventing unauthorized access and minimizing security breaches.
- Auditing and Reporting: The platform generates detailed reports and maintains comprehensive audit trails to demonstrate compliance with policies and regulations.
- Integration and Compatibility: The platform integrates code-signing with popular development tools and pipelines, such as Azure DevOps, Jenkins, and GitLab, automating the process and reducing the risk of manual errors.
- Reproducible Builds: The CodeSign Secure platform facilitates the creation and verification of reproducible builds, ensuring the distributed software is not vulnerable and compromised. It provides the user with assurance regarding the integrity of the source code, ensuring that the software has not been tampered with.
Other Security Measures
There are several processes and steps one can take to reduce the possible impact of a data breach, such as:
-
Develop and Test an Incident Response Plan
- Every organization should have a documented plan for responding to a data breach. This plan must detail roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, data recovery procedures, and notification strategies.
- IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 indicated that firms that executed the response plan without involving law enforcement during ransomware incidents had an average of $470,000 difference in costs and affected numbers of records, which included an additional 33 days in their breach lifecycle (277 days on average).
-
Invest in Security Awareness Training
- It’s important to provide cybersecurity training to employees, covering topics such as phishing prevention, safe password practices, and how to identify and report suspicious behaviour.
- The companies with proper response teams saved an average of $2 million from the breach compared to those with no response teams or testing.
-
Consider Cyber Insurance
- Cyber insurance can provide financial assistance in the aftermath of a data breach, covering costs associated with legal fees, forensics, notification, and potentially credit monitoring for affected individuals.
- Companies should use cyber insurance that aligns with the organisation’s specific needs and requirements that will help them to recover from a data breach.
Conclusion
Data breaches levy an immense financial burden on a company, typically at a level of millions of dollars. Along with financial distress, such breaches also cause harm to the brand, disruptions to work, and any legal implications. Regular cybersecurity measures are insufficient to handle the evolving technological means of ransomware threats. Encryption Consulting’s CodeSign Secure solution provides complete protection against unauthorized code, which contributes to more incidents of data theft and exploitation.
CodeSign Secure ensures secure code signing and enables trust and transparency within the software supply chain. This reduces the likelihood of unknowingly installing compromised code from an unauthorized source. It helps organizations avoid the huge costs associated with disruptions, reputational damage, and potential lawsuits that often follow a major data breach.




